Streamline Store Operations with Smart Retail Technologies
Retailers face growing demands for efficiency, reduced shrinkage, and enhanced customer experiences. By integrating RFID, barcodes, thermal printers, enterprise mobile computers, AI-powered applications, and cloud-based systems, retailers can unify in-store workflows—from inventory management to checkout—while leveraging automation and real-time data for smarter, more flexible operations.
Application ScenariosChoosing the Right DevicesWhy Choose Us
Application Scenarios
1. Checkout and Payment
Technology Used:
- RFID and barcode-enabled self-checkout.
- Mobile POS with enterprise mobile computers.
Use Case:
A retailer utilizes RFID for frictionless self-checkout, where customers can scan all items at once. Store associates use mobile POS devices to check out customers anywhere in the store.
2. Inventory Management and Stock Replenishment
Technology Used:
- RFID handheld readers for real-time inventory tracking.
- Enterprise mobile computers with barcode scanners for stock counting.
- Thermal printers for shelf labels and markdown tags.
Use Case:
A fashion retailer employs RFID handheld readers to quickly verify inventory levels. Enterprise mobile computers allow staff to scan barcodes for stock updates and mobile thermal printers print new price tags for markdowns.
3. Order Fulfillment and Click-and-Collect
Technology Used:
- Barcode and RFID scanning for order picking verification.
- Mobile label printers for pickup order labels.
- Enterprise mobile computers for order management.
Use Case:
A grocery store team scans RFID labels or barcodes to verify BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store) orders. Thermal printers generate order labels for easy identification, and associates use enterprise mobile computers to locate items and update order status.
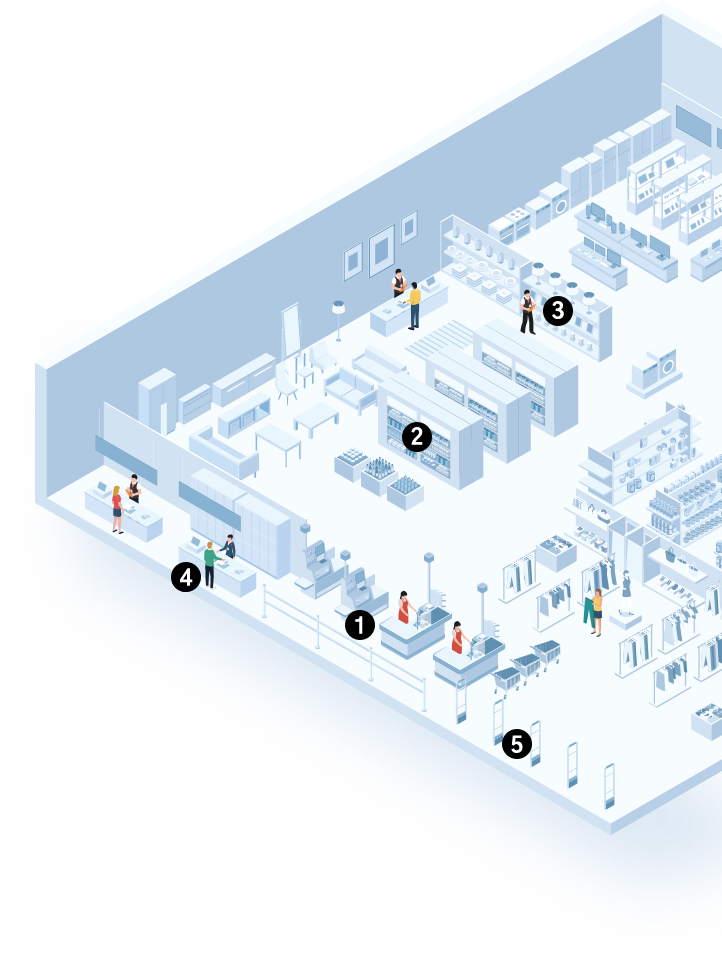
4. Product Returns
Technology Used:
- Barcode and RFID scanning for returns verification.
- Enterprise mobile computers for returns processing.
- Thermal printers for return labels.
- Cloud-based applications for return status tracking.
Use Case:
A retailer processes product returns efficiently, whether in-store or online. Associates scan barcodes/RFID tags, use mobile computers for real-time updates, print return labels, and track statuses via cloud applications, ensuring smooth operations and customer satisfaction.
5. Loss Prevention and Security
Technology Used:
- RFID labels for item tracking and theft detection.
- Barcode/RFID access control for employees.
- Mobile computers for loss prevention audits.
Use Case:
Instead of traditional RFID security tags, a retailer embeds RFID labels in products for theft prevention. Exit readers detect unpaid items. Staff use mobile computers for inventory checks, which can reveal loss patterns and support shrinkage investigations.
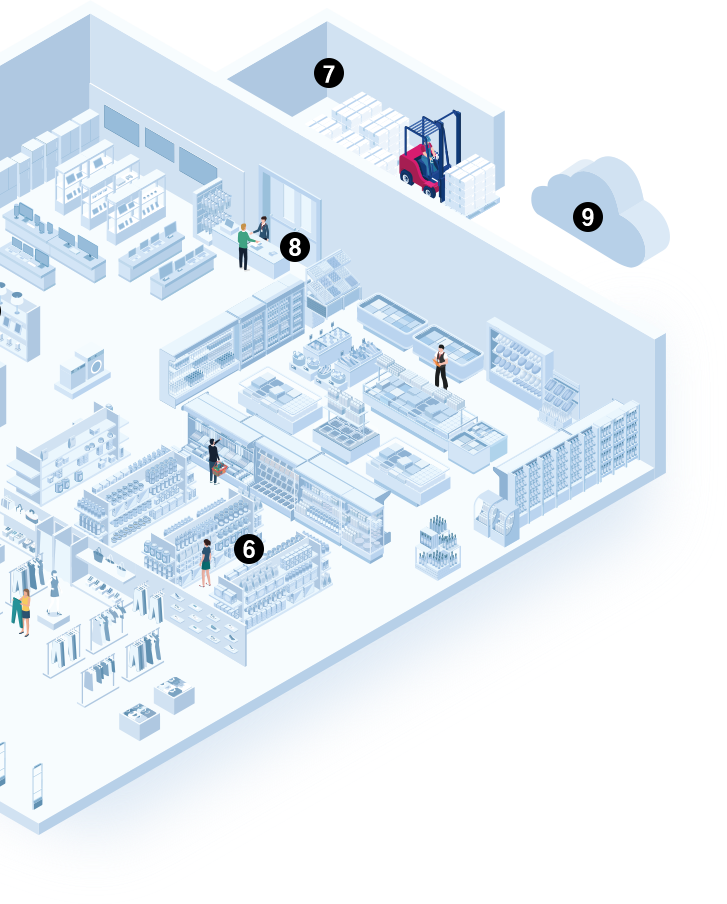
6. Dynamic Pricing and Labeling
Technology Used:
- Thermal printers
- Barcode and RFID technologies
- AI-powered pricing algorithms
Use Case:
AI analyzes customer behavior, market trends, and competitor pricing to dynamically adjust prices. Thermal printers then generate updated labels in-store, ensuring consistent and accurate pricing. Barcodes and RFID ensure real-time synchronization of price changes across all channels for a unified, seamless shopping experience.
7. Backroom Operations – Receiving and Shipping
Technology Used:
- RFID portals for automated receiving and shipping.
- Enterprise mobile computers for put-away and shipment verification.
- Thermal printers for stock and shipping labels.
Use Case:
A retailer receives shipments with RFID-labeled cartons, allowing RFID portals to scan all items at once. Staff use enterprise mobile computers to verify barcodes for put-away and generate new shipping labels using thermal printers before outbound shipments.
8. Customer Engagement and Personalization
Technology Used:
- Enterprise mobile computers (EMCs).
- AI-driven recommendations.
- RFID-enabled smart fitting rooms.
- Barcode-based loyalty program scanning.
Use Case:
AI recommends products based on customer preferences. RFID smart fitting rooms help customers check sizes and styles, while associates use EMCs for personalized assistance. Barcodes enable seamless loyalty rewards and quick checkouts, ensuring a unified in-store and online experience.
9. Cloud and AI In-Store Operations
Technology Used:
- Barcode and RFID technologies
- Enterprise mobile computers (EMCs)
- Cloud-based applications
- AI-powered applications
Use Case:
Cloud systems and AI integrate seamlessly to enable real-time inventory tracking, dynamic stock replenishment, and consistent labeling across stores. Barcodes and RFID ensure data accuracy, while thermal printers create efficient labels. Store associates use EMCs to access cloud data for inventory verification, order management, and customer engagement, driving a unified, efficient omnichannel experience.
Not sure what fits your needs?
Choosing the Right Devices
Equip your stores for success with AIDC devices that match your operations. Consider these four essentials:
Got questions on selection?
Let’s power what is next in retail - together.






































